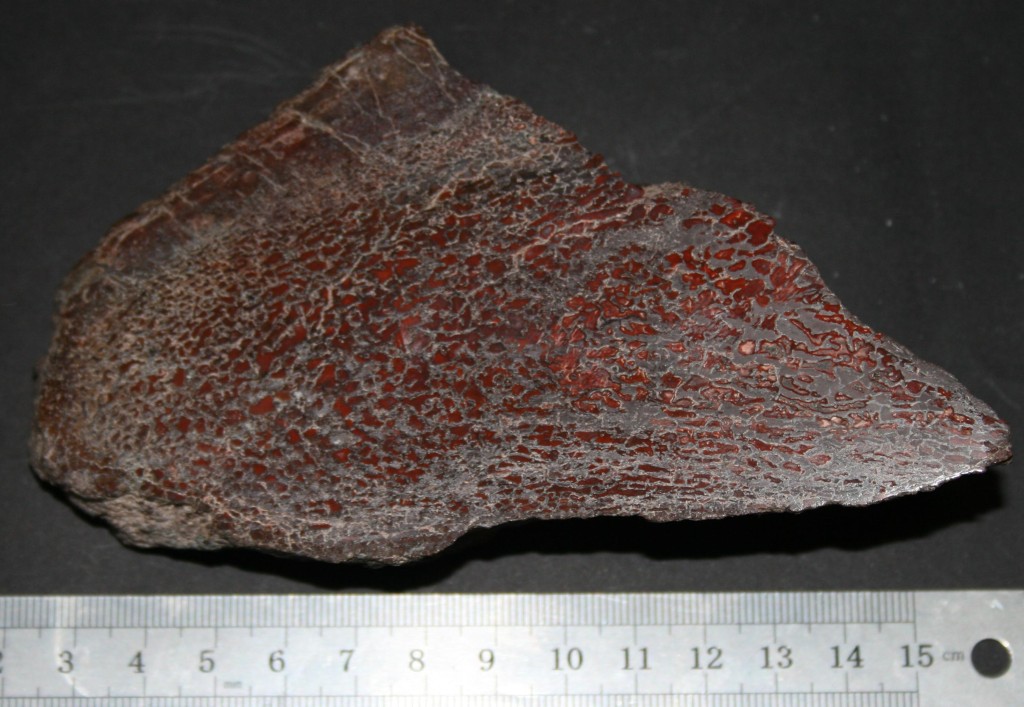

Dinosaur bone
The trabeculae of the original bone (grey areas surrounding the red marrow/fat areas)
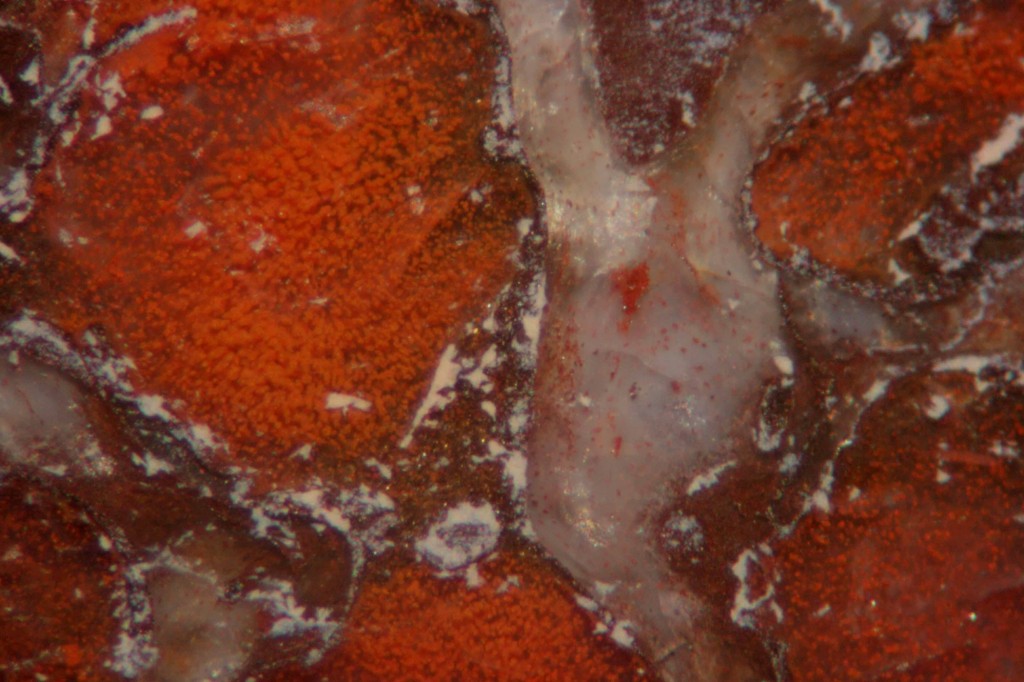

A view of the dinosaur bone
In the previous figure seen under the microscope. The white “Y” shaped area is the old bone. The small red dots within the “Y” are lacunae, in which the bone cells once lived.
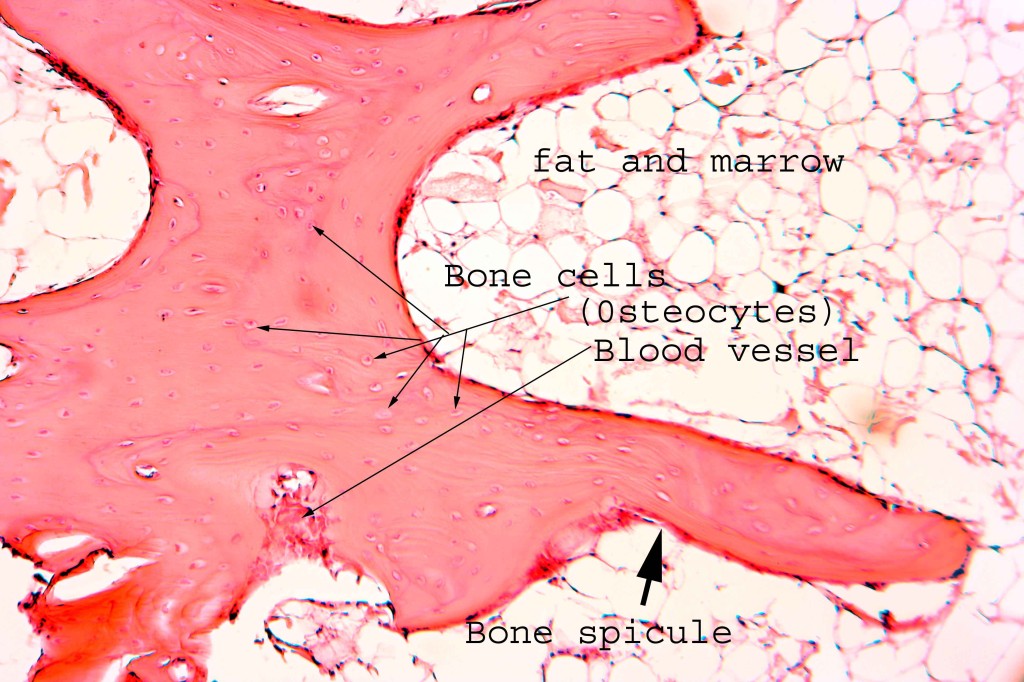
Rabbit bone
For comparison, here is a histological specimen of rabbit bone, The bone in this slide is red and again the lacunae are well seen. The fat and marrow are seen on the right of the slide.
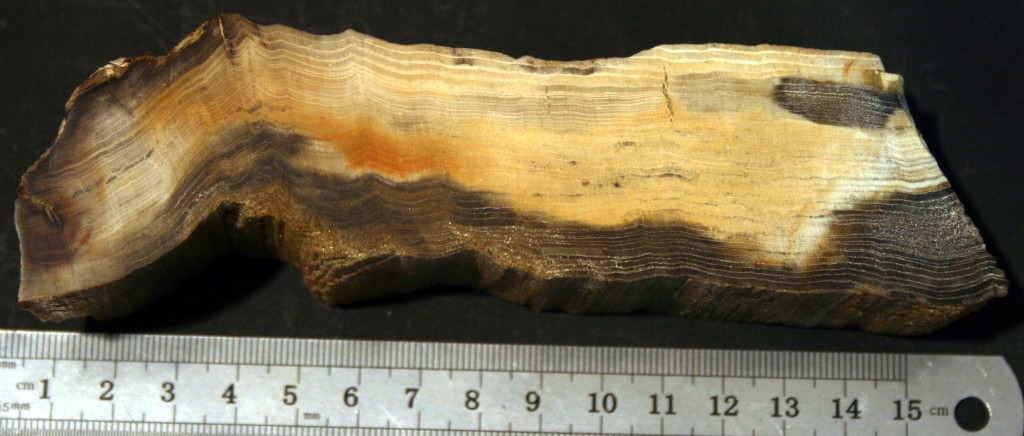

Fossil wood
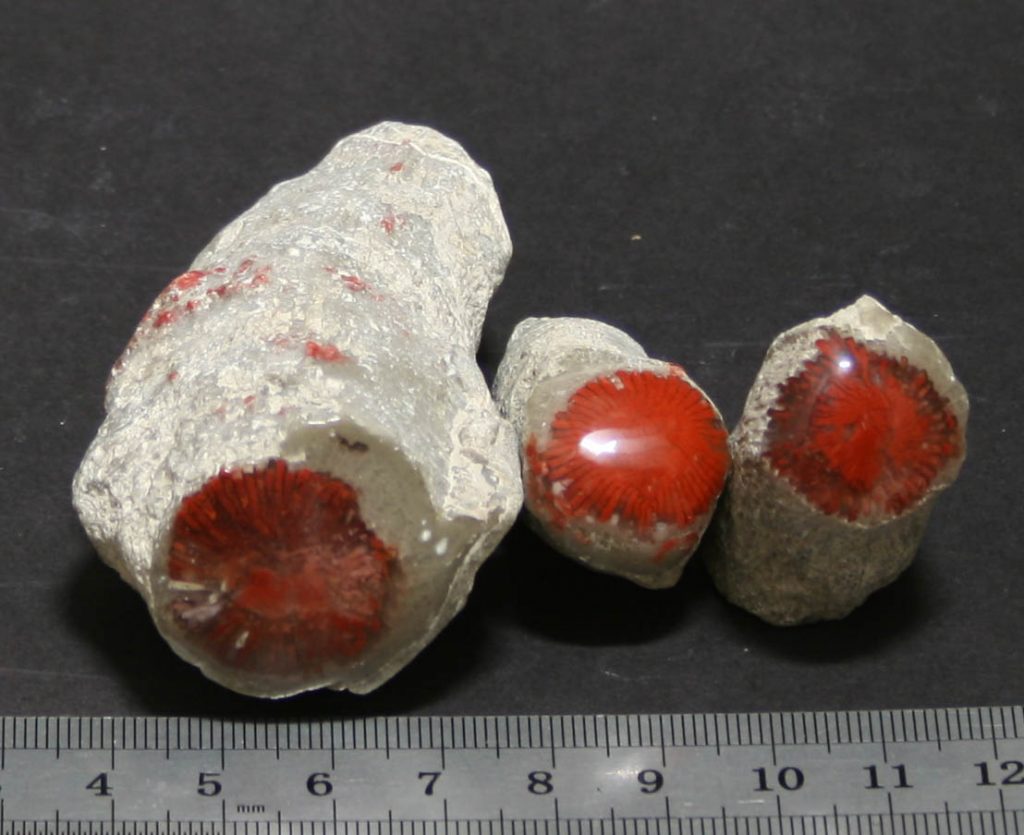

Fossilized coral
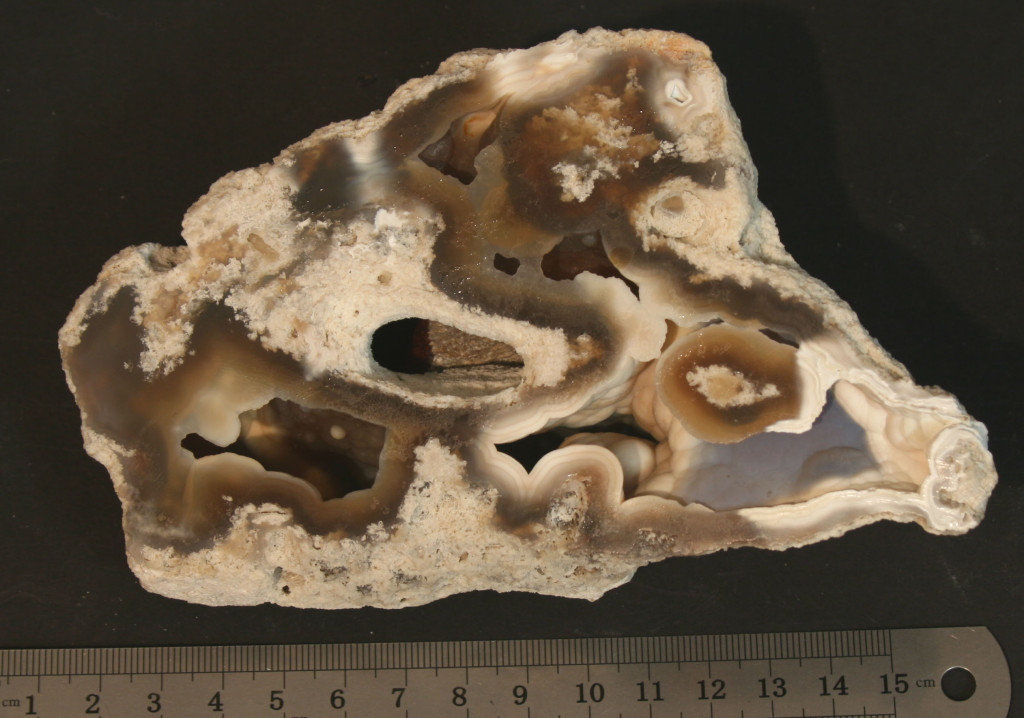

Fossilized coral
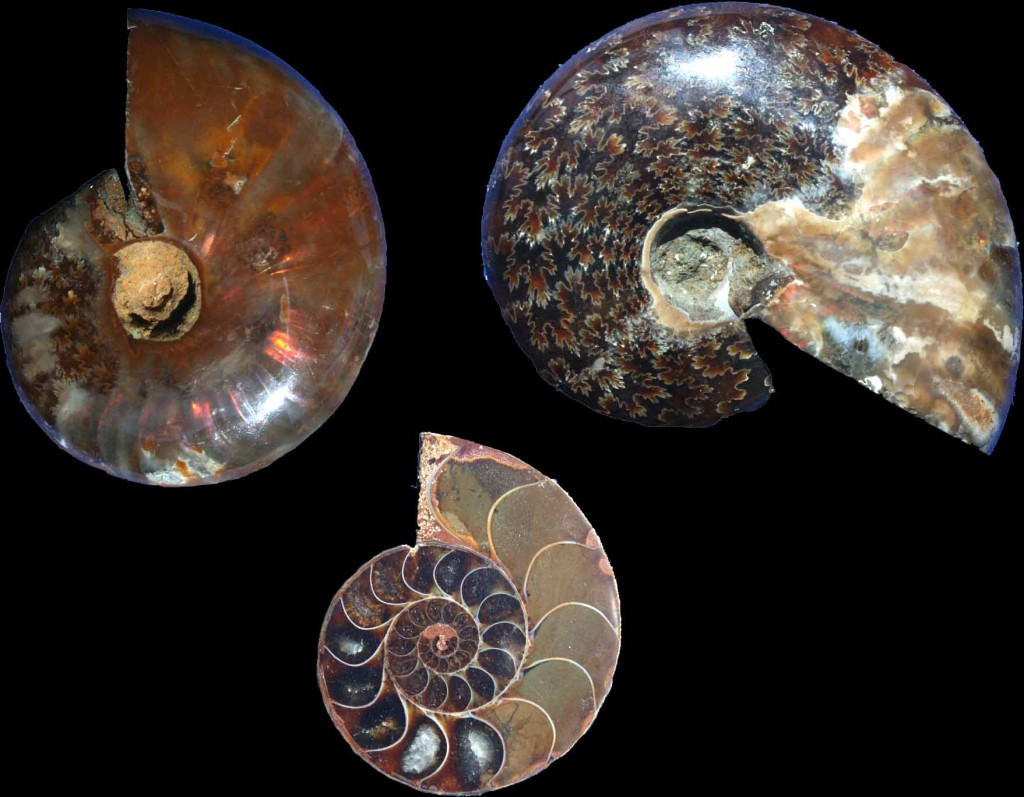
Fossilized ammonites
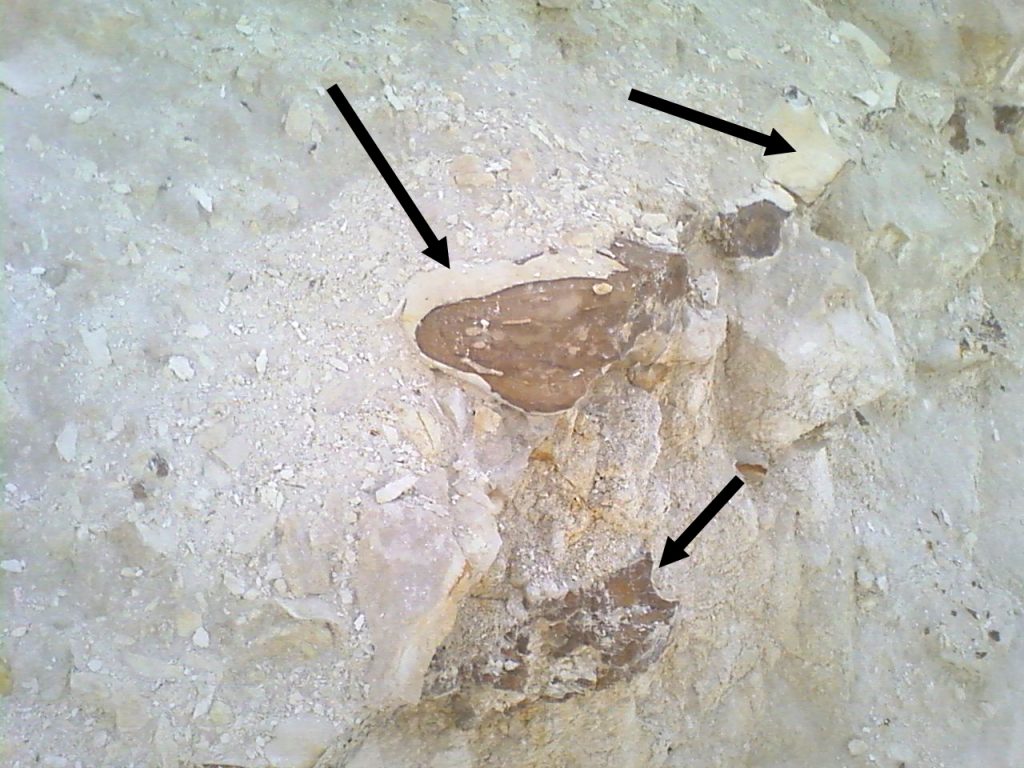

Nodules of chert
Are seen protruding from the Eocene chalk.
It was from this material that Stone age man made his arrows, spears and axes.
Without this, the Ascent of Man would have taken a very different path or not have happened at all.
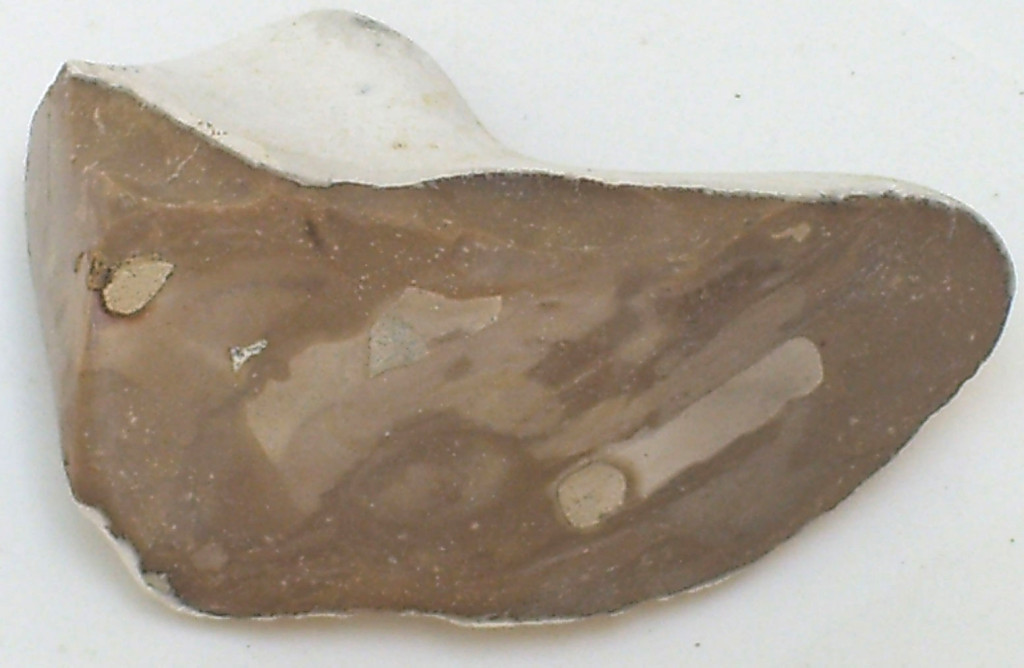

Negev flint
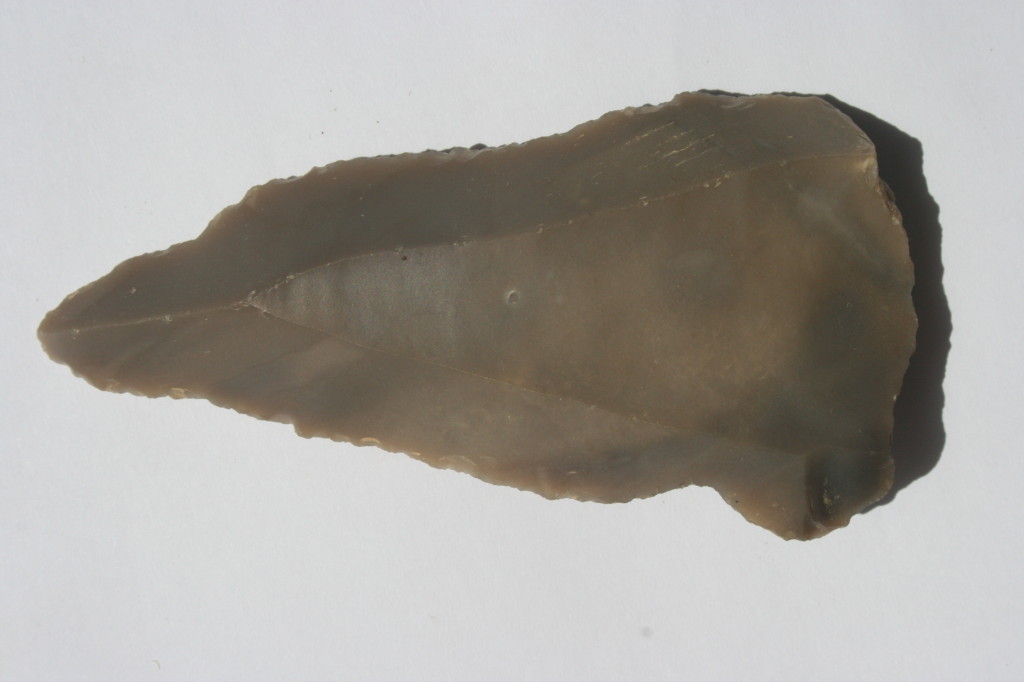

Stone age arrow made from flint

Bulbus
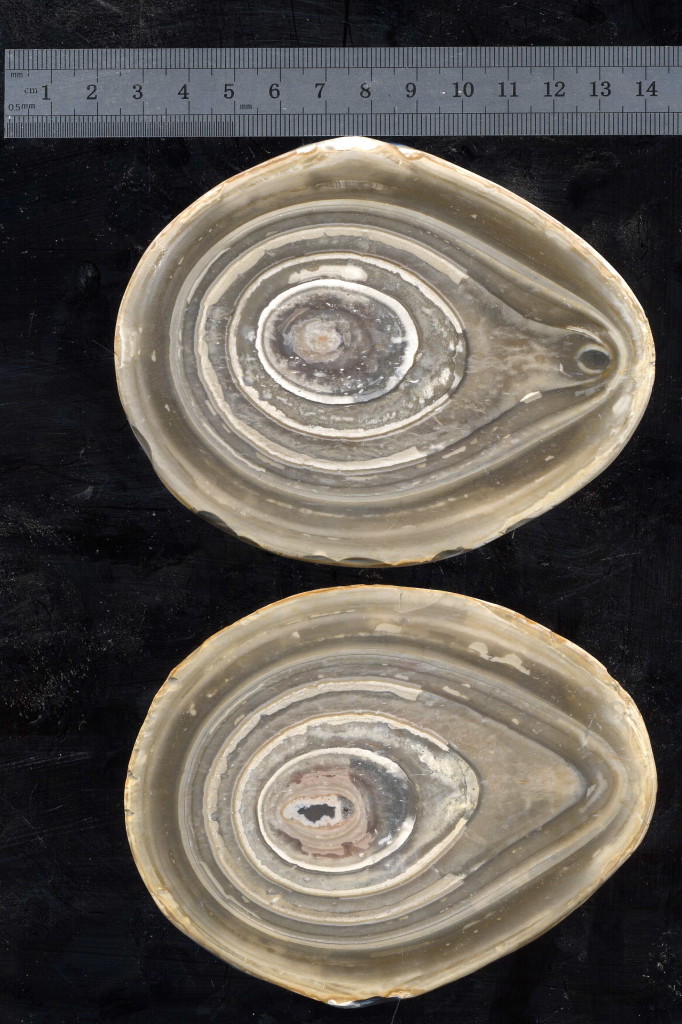

Organic material
Although formed within a marine environment from organic material, the Silica has still “managed” to form an orderly symmetric structure.













